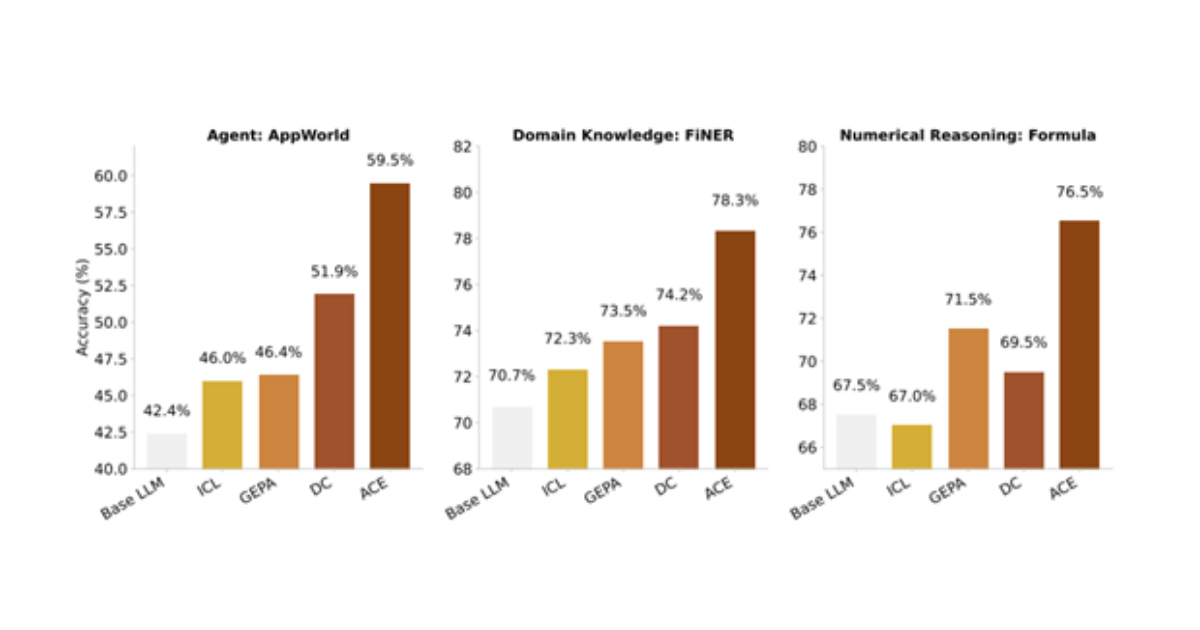
In the fast-paced world of technology, researchers are constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Recently, a team from Stanford University, SambaNova Systems, and UC Berkeley introduced a groundbreaking framework known as Agentic Context Engineering (ACE). This innovative approach aims to enhance large language models (LLMs) by leveraging evolving, structured contexts, rather than relying solely on weight updates. The core concept behind ACE is to enable language models to improve themselves autonomously, eliminating the need for extensive retraining processes.
Traditional methods of enhancing LLMs often involve adjusting the weights within the model based on new data or objectives. While effective, this approach can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. ACE, on the other hand, takes a different path by focusing on the context in which the language model operates. By providing a framework for models to adapt and evolve within specific contexts, researchers believe that ACE has the potential to revolutionize the field of natural language processing.
One of the key advantages of the ACE framework is its ability to facilitate continuous improvement without the need for manual intervention. By allowing language models to self-optimize within predefined contexts, researchers can achieve higher levels of performance and efficiency. This self-improving aspect of ACE opens up new possibilities for applications in various fields, including machine translation, text generation, and sentiment analysis.
Moreover, the approach taken by ACE aligns with the growing emphasis on interpretable and explainable AI systems. By focusing on context and evolution rather than just numerical adjustments, researchers can gain deeper insights into how language models learn and adapt to different scenarios. This increased transparency not only enhances the trustworthiness of AI systems but also paves the way for more ethical and responsible deployment of these technologies.
In a paper detailing the ACE framework, the researchers provide a comprehensive overview of the methodology and its potential implications for the future of LLMs. By combining the expertise of multiple institutions, including Stanford University, SambaNova Systems, and UC Berkeley, the development of ACE represents a collaborative effort to drive innovation in the field of artificial intelligence.
As the tech industry continues to evolve, frameworks like ACE play a crucial role in shaping the next generation of AI technologies. By prioritizing self-improvement and context-driven adaptation, researchers are not only advancing the capabilities of language models but also laying the foundation for more versatile and intelligent AI systems. The introduction of ACE marks a significant milestone in the ongoing quest to unlock the full potential of artificial intelligence and natural language processing.
In conclusion, the ACE framework represents a paradigm shift in the way we approach enhancing large language models. By focusing on agentic context engineering, researchers have opened up new possibilities for self-improvement and autonomous adaptation within AI systems. As the technology landscape continues to evolve, frameworks like ACE will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of artificial intelligence and driving innovation across various industries.

